Vacuum Casting Process for Prototypes: Step-By-Step Guide
What is Vacuum Casting of Prototypes?
Vacuum casting process for prototypes is a production technique in which a silicone mold is produced on a master pattern, and liquid polyurethane resin is vacuum cast. Air bubbles are removed by vacuum, providing a void-free, accurate, and durable piece.
Advantages of Vacuum Casting for Prototypes
Vacuum casting in prototypes also has many benefits and, therefore, has become a favorite in product development and low volumes. It has one of the main advantages, producing the kind of ABS-like prototype parts with realistic mechanical properties. These components replicate closely the product materials, and they give the designers and engineers the true image of the product.
- Vacuum casting can be considered in low-volume manufacturing and short-run production, which is why it is a perfect solution for startups, small businesses, or projects that need less volume. It also enables close tolerances, usually to +-0.2 mm to +-0.5 mm, based on part geometry, to provide accurate performance and reliability in quality functional prototypes.
- There is a decreased time-to-market, which is another advantage. Prototypes could be created in a matter of days with the rapid creation of molds and the casting cycle, and the tipping point of enabling designers to first-cycle and prove their concepts as effective. Complex designs and undercut structures are also assisted by the process and can be difficult or expensive to achieve by means of traditional injection molding.
- Vacuum casting is inexpensive, flexible, and dependable in the overall production of prototypes. It assists the companies in testing, validating, and refining products before they make any investment in producing large quantities.
Materials in the Vacuum Casting Process to Do Prototypes
The appropriate choice of material in the process of vacuum casting prototypes is important in attaining functional, durable, and cosmetically accurate parts. We have a selection of materials available at SunOn: plastics, metals, and composite resins that have been selected due to their mechanical strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability.
- ABS-like, PC, and TPU resins are often used in plastic prototyping, which have realistic mechanical properties as well as surface finishes. Such materials would be suitable for functional testing, design validation, and low-volume production.
- Metal-filled or composite resins may also be used in specialized applications to recreate certain production-grade properties, so that prototypes act like finished goods.
We have materials that are used in automotive, consumer electronics, medical equipment, and aerospace industries, where part performance, durability, and accuracy are important. With flexible material choices, we can guarantee that the vacuum casting process for prototypes satisfies engineering as well as aesthetic needs; this allows designers and engineers to make sound decisions before mass production.
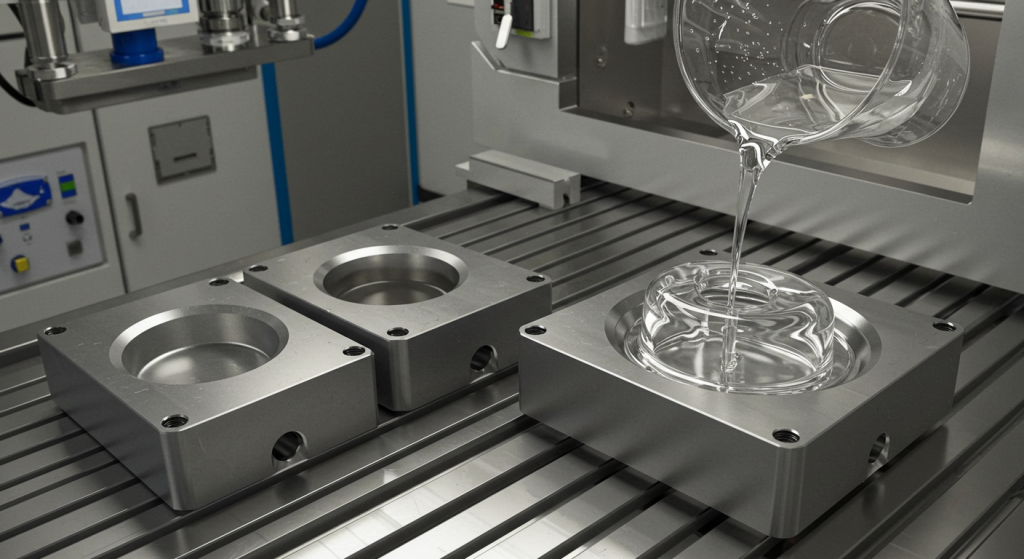
Step-By-Step Process: Vacuum Casting Prototyping
- Master Model Preparation
A pattern CNC master or a 3D model is made. This model is an exact geometry and surface finish of the finished part.
- Silicone Mold Creation
The master model is covered with high-quality silicone of high quality. The mold makes a perfect copy of the fine details and the complicated features once cured.
- Resin Selection & Mixing
Depending on the needed properties, polyurethane resin or other engineering-grade materials are used. The resin is well blended to attain uniformity.
- Vacuum Degassing
Vacuum conditions are applied to the silicone mold into which resin is poured. Vacuum eliminates enclosed air, eliminating lack or voids.
- Curing & Demolding
The parts of the cast are left to dry under regulated temperatures. Parts are then demolded in a process that is careful to preserve shape and detail, once hardened.
Post-Processing & Finishing
- Polishing and surface sanding.
- Painting or coating
- Functional prototyping assembly.
Vacuum Casting Prototypes Uses
- Consumer Electronics
ABS-like smartphone, wearable, and tablet prototypes' housings.
- Automotive Industry
Dashboard, panel, and test part components that are ABS functional low-volume components.
- Medical Devices
Surgical instrument and diagnostic equipment prototype casings.
- Aerospace & Industrial
Multifaceted mini batch prototype parts of UAVs, machinery, and enclosures.
Why SunOn Industrial Group?
- More than 10 years’ experience in prototype vacuum casting.
- ISO9001, IATF16949, ISO14001 certified.
- Serves consumer electronics, automotive, medical, and aerospace prototyping.
- Provides a complete master model to post-processing/assembly services.
Guidelines for Maximizing Your Prototype Vacuum Casting
With maximum optimization of your prototype vacuum casting process, high-quality parts, accurate testing, and reduced development cycles are achieved. These are some of the most important guidelines to get maximum results:
- Find the Right Resin - Find a resin that fits your part in terms of the mechanical strength, flexibility, and surface finish. The right material is used to come up with realistic prototypes that operate with the production parts.
- Optimize Mold Design - Design molds that are easy to demold, have few defects, and free-flowing resin. Undercuts, draft angles, and venting may be considered to minimize the amount of bubbles and enhance the quality of surfaces.
- Post-Processing Plan - Expect other activities that may require the use of paint or polishing, or assembling. By doing post-processing early, you are sure that your prototypes will impress you in terms of both visual and functional appearance.
- Communicate Tolerances Understandably - Be specific with critical features tolerances to ensure that parts fit when put to functional use and verification. Effective communication eliminates expensive changes in the future.
- Leverage Small Batch Runs - Small batch production is used to test designs before injection molding. This process minimizes risk, establishes manufacturability, and makes it possible to run design iterations without incurring the high tooling costs.
Conclusion
The vacuum casting process for prototypes is a rapid, inexpensive, and adaptable solution to manufacturing high-quality ABS-like products. It is best suited to low-volume, functional prototypes in electronics, automotive, medical, and aerospace industries. Through the experience of SunOn Industrial Group, businesses can speed up the development of products, minimize risks, and realize high-quality products within low turnaround periods. Get to know more about our vacuum casting and rapid prototyping services at SunOn Industrial Group.

